| In 1953, Loeb and Sorirajan first prepared a high water flux (Water Flux, WF) and a high salt rejection (Salt Rejection, SR) cellulose acetate reverse osmosis membrane, thus laying the basis of reverse osmosis technology, which led to the rapid development of other membrane programs.
In the mid-fifties, a scientist, Dr. S. Sourirajan, at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) invented the "artificial imitation of biological selective membrane". This was the first time humans could use the principle of reverse osmosis. The US federal government invested in the region of 4 billion dollars in the successful research of the use of the principles of reverse osmosis on sewage pressure, so that only pure water molecules, and not harmful substances emissions, could penetrate the membrane to produce pure water.
The first time NASA used the process was on the space shuttle, where they were able to reclaim the astronauts’ urine and sewage and then purify it for drinking. It is also used on aircraft carriers and in submarines, and for desalination for soldiers to drink, as well as being used to provide drinking water for ordinary families in the United States. This breakthrough in human drinking water and sales around the world prove its reliability.
The first batches of reverse osmosis membranes were used in the 1950s, primarily in the desalination industry, but the cost of distillation was high. Their performance and potential was immediately discovered by the US Department of NASA and their development was funded to solve the problem of spacecraft drinking water.
From the 1970s, the low-pressure osmotic membrane started to appear and the first batch of small household reverse osmosis drinking water purifiers also began production. These were able to purify about one to five liters of drinking water per day, and were able to effectively solve the US central and southern desert areas problems caused by nuclear radiation pollution of the water.
Today, home reverse osmosis equipment is able to provide 285 liters (about 75 gallons) of drinking water a day, enough to meet the drinking and cooking needs of a small family or office. In addition the change in water pressure from the first generation’s high pressure down to the present 50 pounds per square inch of fifty pounds of water pressure (50PSI) makes it suitable for general use and for tap water pressure.
The development history of the reverse osmosis membrane is shown in Table 1. |
Table 1. History of reverse osmosis membranes
|
| Year |
Inventor |
Research or Invention |
| 1748 |
French scientists |
Discovered that porcine gallbladder can penetrate the phenomenon of water. |
| 1861 |
Graham |
Discovered the dialysis phenomenon and began its study. |
| 1903 |
Morse and Pierce |
Introduced the electrode into the dialyzer and thus began the study of electrodialysis. |
| 1906 |
Bechhold |
Manufactured an ultrafiltration membrane with a pore size of 0.01 μ (micron). |
| 1913 |
Abel |
Proposed the use of a hollow fiber dialyzer (Dialyzer) as an artificial kidney concept. |
| 1943 |
Kolff |
Successfully completed the idea of artificial kidney and is known as the father of artificial organs. |
| 1950 |
Dr. S Sourirajan(UCLA) |
Invented the "artificial pseudo-selective selective permeability membrane", that is, the principle of reverse osmosis. |
| 1953 |
Reid |
Began research on reverse osmosis procedures. |
| 1960 |
Loeb & Souriraja |
First to fabricate a cellulose acetate reverse osmosis membrane with high water flux (Water Flux, WF) and high rejection (Salt Rejection, SR), thus laying the foundation for reverse osmosis membrane technology. |
| 1970 |
Israel Desalination Engineering Company |
Proposed hybrid filter (Hybrid Filteration) of the term, this is the first pole filter concept. |
| 1970 |
Filmtec Company(a subsidiary of Dow Chemical) |
Invented the low pressure reverse osmosis membrane.
|
|
| Source: Lin Dongpo master thesis |

|
In 1748 French scientists first discovered the phenomenon that water can permeate a pig’s gallbladder but, based on the production technology of the time, this knowledge could not be used in a practical way. This phenomenon was used over the next two hundred years to explain other various natural phenomena, such as the theory on how trees absorb moisture. The principle is as follows:
If the permeate membrane separates brine on two sides with different concentrations, the water molecules will move from the low concentration side to the high concentration side in order to balance the potential energy on both sides, until the water level and water pressure difference between the two sides are equal whereby water molecules cannot be relocated and material exchange is balanced. This is the osmotic effect (Osmosis) phenomenon. Such as 4.11.
|
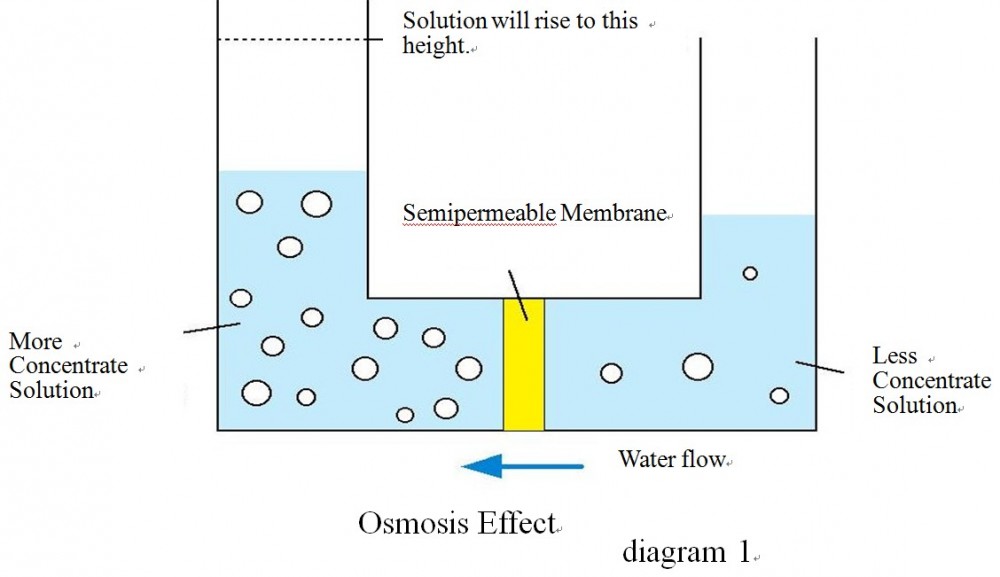 FIGURE 4.11 The phenomena of thin membrane permeation FIGURE 4.11 The phenomena of thin membrane permeation
Data source: http://www.alamowater.com/development/PDFs%20website/Reverse%20101.doc |
Reverse osmosis, as its name implies, is able to stop the above mentioned infiltration effect, such as pressure moving from the high concentration side and reverse it, so that the water from the high concentration side is forced to the low concentration side for water purification. As shown in Figure 4.12. |
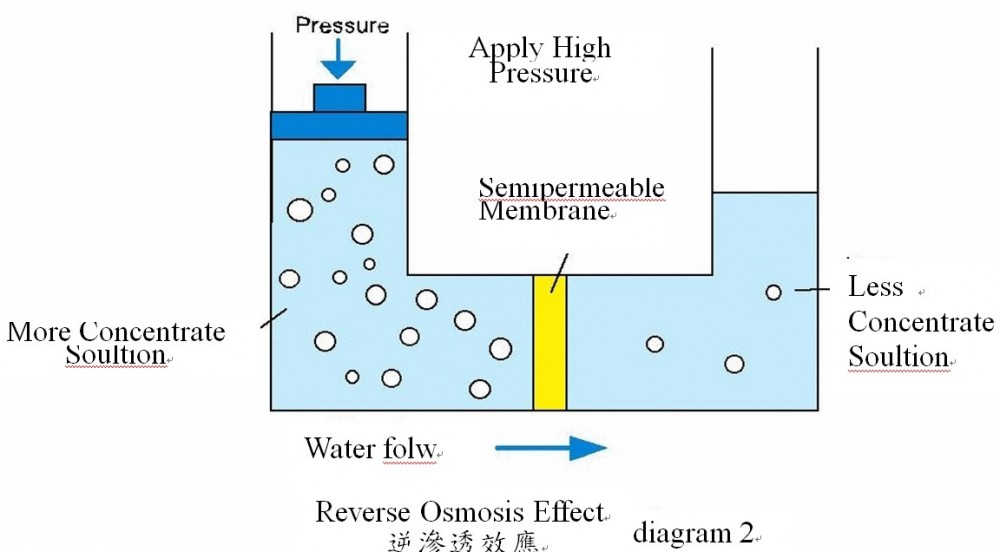
FIGURE 4.12 The phenomena of permeation
Data source: http://www.alamowater.com/development/PDFs%20website/Reverse%20101.doc |
In simple terms, in the raw water side of the application the pressure is greater than in reverse osmosis. In reverse osmosis, contaminated components concentrated in the raw water such as: dissolved and insoluble inorganic salts, heavy metals, organic matter, bacteria, and particles cannot pass through the semipermeable membrane. Only water molecules and smaller molecules of salt can penetrate the film, and flow to the water on the other side.
To concentrate raw water the pressure has to be gradually and infinitely increased. In actual operation, if you could continue to supply raw water to maintain a constant pressure you could drain the concentrate and achieve the purpose of reverse osmosis.
When it comes to the reverse osmosis membrane, it is included in a small part of the separation membrane. The separation membrane (CROSS-FLOW) can be subdivided into: Refer to Table 4.16.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO)
- Ultra Filtration (UF)
- Microfiltration (MF)
- GAS Separation (GS)
In all separation membrane projects reverse osmosis membrane permeability holes are the smallest, between 0.0001 ~ 0.002 micron. For comparison the human hair has a diameter of about 10micron. You can therefore see the precision in the reverse osmosis membrane pore. In addition it effectively filters bacterial viruses and also removes toxic heavy metals in water, as shown in Figure 4.13 separation membrane application and Table 4.16 separation membrane type. |
Table 4.16 Types of separation membrane
|
| NO. |
Abbreviation |
Separation membrane English name |
Chinese name |
Water permeation porous diameter (MICRON) |
| 1 |
RO |
REVERSE OSMOSIS |
逆滲透 |
0.0001 ~ 0.002 |
| 2 |
UF |
ULTRAFILTRATION |
超過濾 |
0.006 ~ 0.11 |
| 3 |
MF |
MICROFILTRATION |
微孔過濾 |
0.08 ~ 1.2 |
| 4 |
ED |
ELECTRODIALYSIS |
電滲析(或稱電透析) |
---- |
| 5 |
DD |
DIFFUSION DIALYSIS |
擴散滲析 |
---- |
| 6 |
PV |
PERVAPORATION |
滲透蒸發 |
---- |
| 7 |
GS |
GAS SEPERATION |
氣體分離 |
---- |
| 8 |
EDI |
ELECTRODEIONIZATION |
電除鹽 |
---- |
| 9 |
NF |
NANOFILTRATION |
極濾膜 |
0.0009 ~ 0.009 |
|
Data Source: consolidated by EASY WELL |
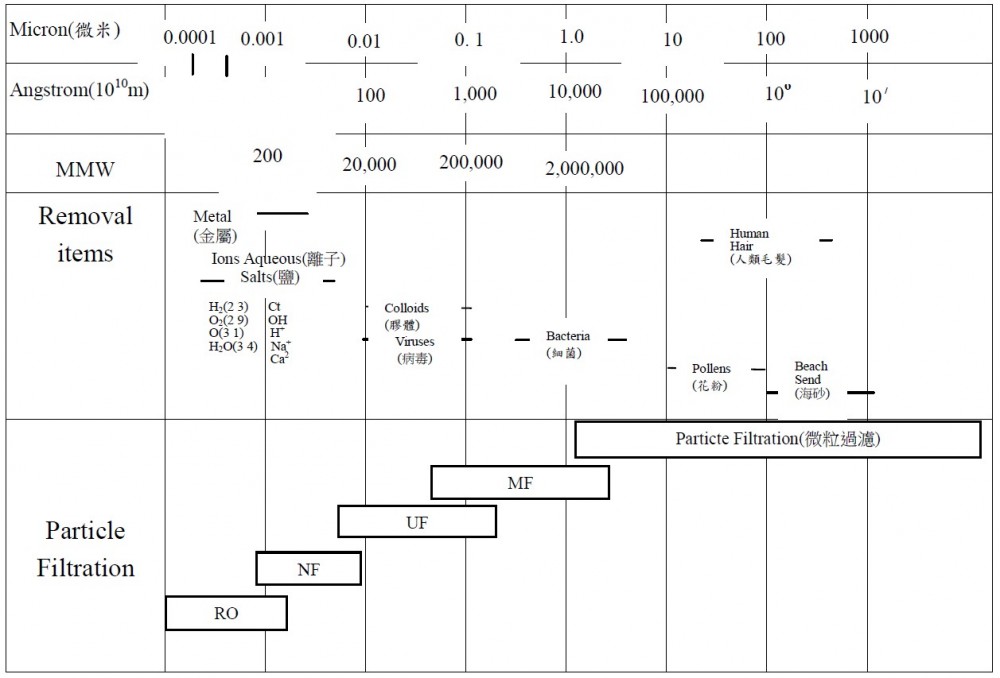
FIGURE 4.13 Application of separation membrane
(Source: Lin Dongpo Master's thesis) |
R.O. (reverse osmosis method) is the great invention of human beings in the 21 centuries. It is the most advanced and safest water filtration method. The main reasons are that R.O. reverse osmosis method is the alternates of the following products.
1. Ion exchanger resin.
2. Distill water machine.
3. Water softening device.
4. UV disinfection machine.
5. Activated carbon water filter.
6. Water filtration canister. |
| |

|
|
1. Be able to remove bacterial, virus, chemical contaminant substances from water, especially those that are difficult to treat heavy metal contaminants such as mercury, arsenic, lead ¡K etc. It lowers the possibilities of developing cancer and all chronic diseases.
2. The water molecule group is smaller than that in the original water, easy to absorb.
3. Impurities content low in pure and clean water, will not increase load in kidney.
4. Good taste no odor, drinks better than common water.
5. At the present time, the use of reverse osmosis method is recognized as the safest drinking water in the world, for home drinking of potable water, make milks, tea, medical use and prevent diseases.
|
|
In general, home use RO water purification machine has two to three pre-filters (stage 1 is a 5 um filter, stage 2 is an activated carbon filter, some model has a third stage 1 um filter). For some machine, a final activated carbon filter is installed between the clean water storage tank and gooseneck faucet. The first stage filter is used to remove sediments and sand etc. particles from water. The activated carbon pre-filter is used to remove organics, odorous molecules and chlorine etc. from water. RO membrane can remove most of the dissolved impurities from water. The final activated carbon filter is used to further remove residue contaminants after RO membrane. Use the semi-permeation principle, add pressure to the feed water and force it flow through the semi-permeation membrane to the clean waterside and leave impurities at the other side and be discharged with wastewater.
Since most of the osmosis membranes are synthetic organic materials, to protect the life of osmosis membranes, there shall be residue chlorine removal units in front of the osmosis membrane. Normally, it is accomplished through the use of activated carbon filters. And, to prevent suspended particles blockage problems, a 5 um filter is installed in front of the activated carbon filter. The pre-activated carbon filter and particle filter can remove larger particles. And, the other substances, such as heavy metals, insecticides, bacterial, virus etc. substances toxic to human bodies, and hardness and odor etc. chemical substances that can affect taste are removed by the RO membrane.
Although RO treatment method is the complete method, among all types water purifiers, that can remove all contaminants in water, however, the area between the water storage tank and the water faucet, is the location most accessible to contamination by microorganism. Thus, some companies installed UV disinfection light to prevent bio contamination by pathogen microorganism. |

|
|
※ Reverse Osmosis Filtration Process
|
 |
|
From Table 4.17 we can see that reverse osmosis method is one water treatment method that cane be used to remove contaminates.
|
Table 4.17 Comparison of all types of water treatment method
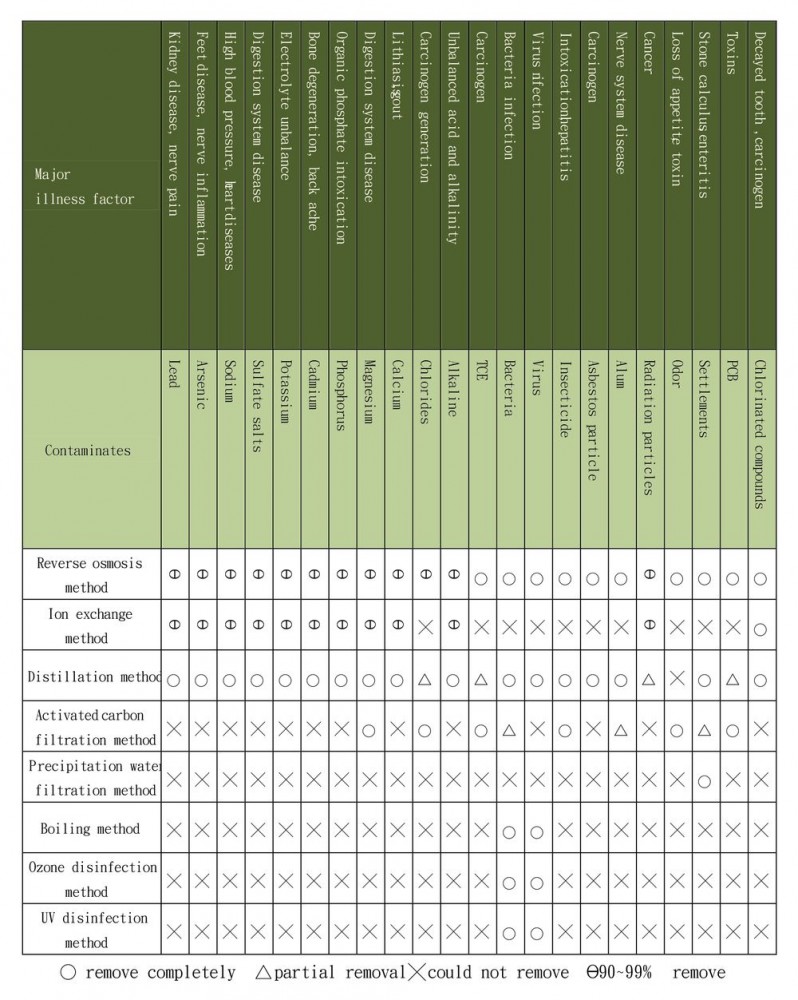
Data source: Consolidated by this research |
|
