 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 TDS (Total dissolved solids) Total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in a liquid. This includes anything present in the water other than the pure H20 molecules. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be a general indicator of water quality. Therefore, High TDS means many substances in the water. Unit:parts per million (ppm). |
 |
| pH hydrogen ion concentration In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
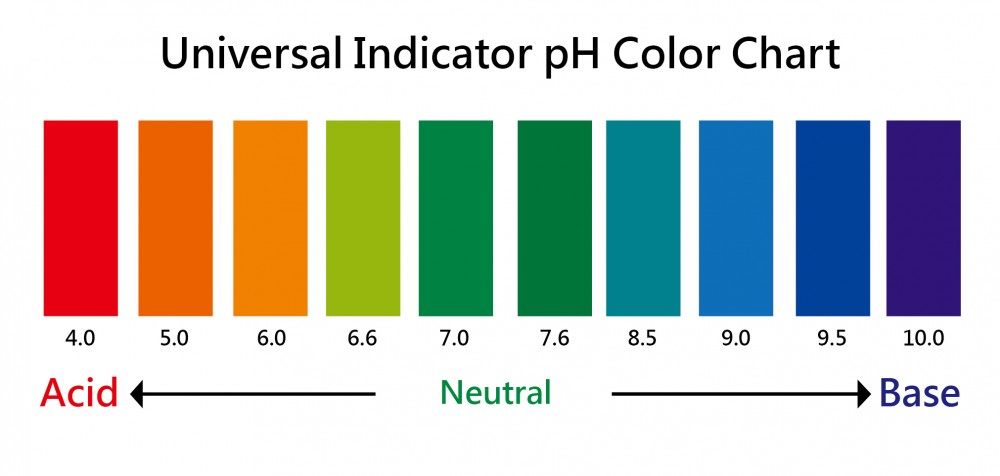 |
 |
|
Chlorine Residual That portion of the total available chlorine residual remaining in water or wastewater at the end of a specified contact period. Chlorine residual will react chemically and biologically as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) or hypochlorite ion (OCl–). This does not include chlorine that has combined with ammonia, nitrogen, or other compounds. 1. At 30 minutes after the addition of sodium hypochlorite there should be no more than 2.0 mg/L of free chlorine residua l present (this ensures the water does not have an unpleasant taste or odor). 2. At 24 hours after the addition of sodium hypochlorite to containers that are used by families to store water there should be a minimum of 0.2 mg/L of free chlorine residual present (this ensures microbiologically clean water). |
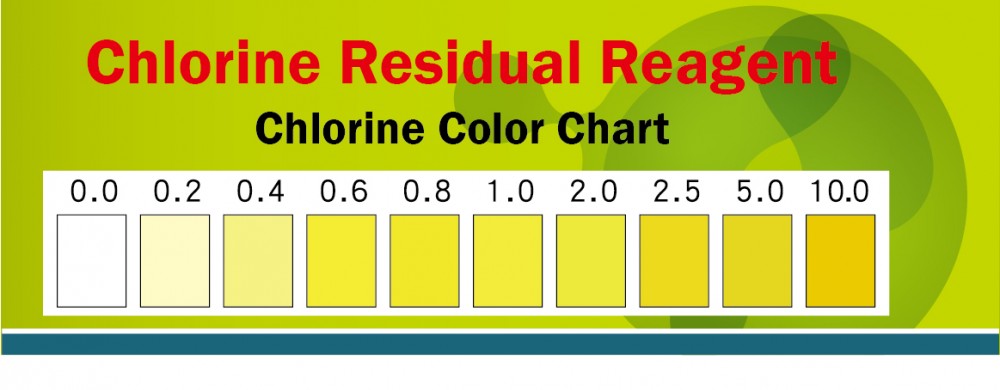 |
 |
|
Hard Water Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. Water is an excellent solvent and readily dissolves minerals it comes in contact with. As water moves through soil and rock, it dissolves very small amounts of minerals and holds them in solution. Calcium and magnesium dissolved in water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard." |
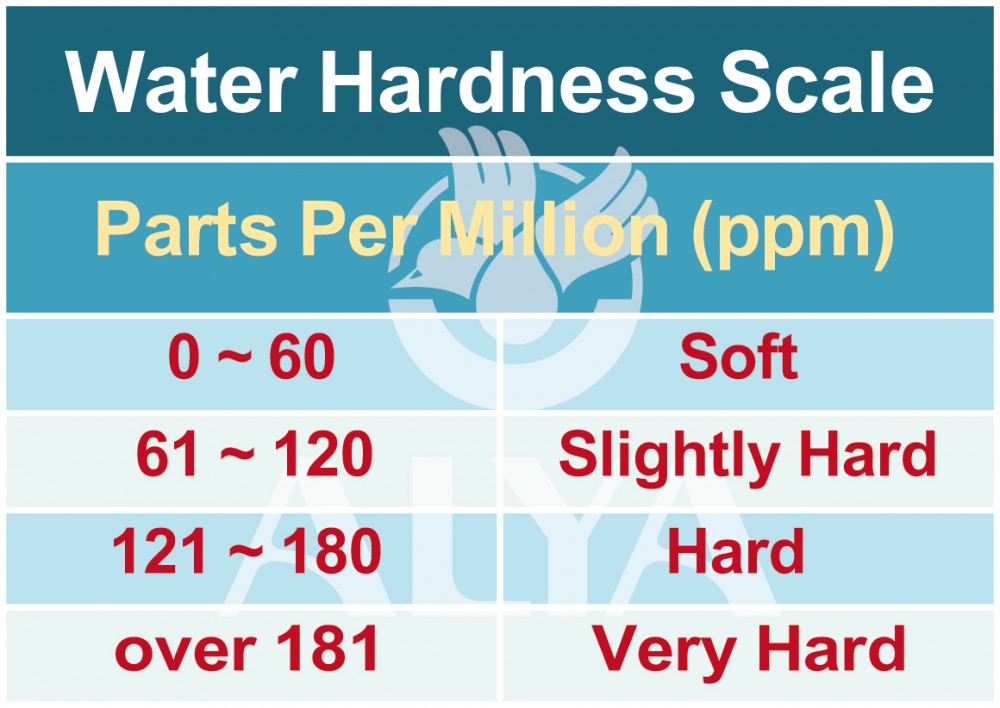 |
 |
|
Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of relative clarity of a liquid. It means the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is an optical characteristic of water and is an expression of the amount of light that is scattered by material in the water when a light is shined through the water sample. The higher the intensity of scattered light, the higher the turbidity. That measurement of turbidity is important test of water quality. |
 |
|
 |
|
 TDS (Total dissolved solids) Total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in a liquid. This includes anything present in the water other than the pure H20 molecules. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be a general indicator of water quality. Therefore, High TDS means many substances in the water. Unit:parts per million (ppm). |
 |
| pH hydrogen ion concentration In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
 |
 |
|
Chlorine Residual That portion of the total available chlorine residual remaining in water or wastewater at the end of a specified contact period. Chlorine residual will react chemically and biologically as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) or hypochlorite ion (OCl–). This does not include chlorine that has combined with ammonia, nitrogen, or other compounds. 1. At 30 minutes after the addition of sodium hypochlorite there should be no more than 2.0 mg/L of free chlorine residua l present (this ensures the water does not have an unpleasant taste or odor). 2. At 24 hours after the addition of sodium hypochlorite to containers that are used by families to store water there should be a minimum of 0.2 mg/L of free chlorine residual present (this ensures microbiologically clean water). |
 |
 |
|
Hard Water Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. Water is an excellent solvent and readily dissolves minerals it comes in contact with. As water moves through soil and rock, it dissolves very small amounts of minerals and holds them in solution. Calcium and magnesium dissolved in water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard." |
 |
 |
|
Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of relative clarity of a liquid. It means the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is an optical characteristic of water and is an expression of the amount of light that is scattered by material in the water when a light is shined through the water sample. The higher the intensity of scattered light, the higher the turbidity. That measurement of turbidity is important test of water quality. |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 TDS (Total dissolved solids) Total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in a liquid. This includes anything present in the water other than the pure H20 molecules. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be a general indicator of water quality. Therefore, High TDS means many substances in the water. Unit:parts per million (ppm). |
 |
| pH hydrogen ion concentration In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
 |
 |
|
Chlorine Residual That portion of the total available chlorine residual remaining in water or wastewater at the end of a specified contact period. Chlorine residual will react chemically and biologically as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) or hypochlorite ion (OCl–). This does not include chlorine that has combined with ammonia, nitrogen, or other compounds. 1. At 30 minutes after the addition of sodium hypochlorite there should be no more than 2.0 mg/L of free chlorine residua l present (this ensures the water does not have an unpleasant taste or odor). 2. At 24 hours after the addition of sodium hypochlorite to containers that are used by families to store water there should be a minimum of 0.2 mg/L of free chlorine residual present (this ensures microbiologically clean water). |
 |
 |
|
Hard Water Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. Water is an excellent solvent and readily dissolves minerals it comes in contact with. As water moves through soil and rock, it dissolves very small amounts of minerals and holds them in solution. Calcium and magnesium dissolved in water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard." |
 |
 |
|
Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of relative clarity of a liquid. It means the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is an optical characteristic of water and is an expression of the amount of light that is scattered by material in the water when a light is shined through the water sample. The higher the intensity of scattered light, the higher the turbidity. That measurement of turbidity is important test of water quality. |
|
 TDS (Total dissolved solids) Total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in a liquid. This includes anything present in the water other than the pure H20 molecules. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be a general indicator of water quality. Therefore, High TDS means many substances in the water. Unit:parts per million (ppm). |
 |
| pH hydrogen ion concentration In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
 |
 |
|
Chlorine Residual That portion of the total available chlorine residual remaining in water or wastewater at the end of a specified contact period. Chlorine residual will react chemically and biologically as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) or hypochlorite ion (OCl–). This does not include chlorine that has combined with ammonia, nitrogen, or other compounds. 1. At 30 minutes after the addition of sodium hypochlorite there should be no more than 2.0 mg/L of free chlorine residua l present (this ensures the water does not have an unpleasant taste or odor). 2. At 24 hours after the addition of sodium hypochlorite to containers that are used by families to store water there should be a minimum of 0.2 mg/L of free chlorine residual present (this ensures microbiologically clean water). |
 |
 |
|
Hard Water Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. Water is an excellent solvent and readily dissolves minerals it comes in contact with. As water moves through soil and rock, it dissolves very small amounts of minerals and holds them in solution. Calcium and magnesium dissolved in water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard." |
 |
 |
|
Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of relative clarity of a liquid. It means the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is an optical characteristic of water and is an expression of the amount of light that is scattered by material in the water when a light is shined through the water sample. The higher the intensity of scattered light, the higher the turbidity. That measurement of turbidity is important test of water quality. |
 |
|
 TDS (Total dissolved solids) Total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in a liquid. This includes anything present in the water other than the pure H20 molecules. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be a general indicator of water quality. Therefore, High TDS means many substances in the water. Unit:parts per million (ppm). |
 |
| pH hydrogen ion concentration In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
 |
 |
|
Chlorine Residual That portion of the total available chlorine residual remaining in water or wastewater at the end of a specified contact period. Chlorine residual will react chemically and biologically as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) or hypochlorite ion (OCl–). This does not include chlorine that has combined with ammonia, nitrogen, or other compounds. 1. At 30 minutes after the addition of sodium hypochlorite there should be no more than 2.0 mg/L of free chlorine residua l present (this ensures the water does not have an unpleasant taste or odor). 2. At 24 hours after the addition of sodium hypochlorite to containers that are used by families to store water there should be a minimum of 0.2 mg/L of free chlorine residual present (this ensures microbiologically clean water). |
 |
 |
|
Hard Water Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. Water is an excellent solvent and readily dissolves minerals it comes in contact with. As water moves through soil and rock, it dissolves very small amounts of minerals and holds them in solution. Calcium and magnesium dissolved in water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard." |
 |
 |
|
Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of relative clarity of a liquid. It means the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is an optical characteristic of water and is an expression of the amount of light that is scattered by material in the water when a light is shined through the water sample. The higher the intensity of scattered light, the higher the turbidity. That measurement of turbidity is important test of water quality. |
|
 TDS (Total dissolved solids) Total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in a liquid. This includes anything present in the water other than the pure H20 molecules. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be a general indicator of water quality. Therefore, High TDS means many substances in the water. Unit:parts per million (ppm). |
 |
| pH hydrogen ion concentration In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
 |
 |
|
Chlorine Residual That portion of the total available chlorine residual remaining in water or wastewater at the end of a specified contact period. Chlorine residual will react chemically and biologically as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) or hypochlorite ion (OCl–). This does not include chlorine that has combined with ammonia, nitrogen, or other compounds. 1. At 30 minutes after the addition of sodium hypochlorite there should be no more than 2.0 mg/L of free chlorine residua l present (this ensures the water does not have an unpleasant taste or odor). 2. At 24 hours after the addition of sodium hypochlorite to containers that are used by families to store water there should be a minimum of 0.2 mg/L of free chlorine residual present (this ensures microbiologically clean water). |
 |
 |
|
Hard Water Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. Water is an excellent solvent and readily dissolves minerals it comes in contact with. As water moves through soil and rock, it dissolves very small amounts of minerals and holds them in solution. Calcium and magnesium dissolved in water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard." |
 |
 |
|
Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of relative clarity of a liquid. It means the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is an optical characteristic of water and is an expression of the amount of light that is scattered by material in the water when a light is shined through the water sample. The higher the intensity of scattered light, the higher the turbidity. That measurement of turbidity is important test of water quality. |
|
 TDS (Total dissolved solids) Total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in a liquid. This includes anything present in the water other than the pure H20 molecules. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be a general indicator of water quality. Therefore, High TDS means many substances in the water. Unit:parts per million (ppm). |
 |
| pH hydrogen ion concentration In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
 |
 |
|
Chlorine Residual That portion of the total available chlorine residual remaining in water or wastewater at the end of a specified contact period. Chlorine residual will react chemically and biologically as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) or hypochlorite ion (OCl–). This does not include chlorine that has combined with ammonia, nitrogen, or other compounds. 1. At 30 minutes after the addition of sodium hypochlorite there should be no more than 2.0 mg/L of free chlorine residua l present (this ensures the water does not have an unpleasant taste or odor). 2. At 24 hours after the addition of sodium hypochlorite to containers that are used by families to store water there should be a minimum of 0.2 mg/L of free chlorine residual present (this ensures microbiologically clean water). |
 |
 |
|
Hard Water Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. Water is an excellent solvent and readily dissolves minerals it comes in contact with. As water moves through soil and rock, it dissolves very small amounts of minerals and holds them in solution. Calcium and magnesium dissolved in water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard." |
 |
 |
|
Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of relative clarity of a liquid. It means the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is an optical characteristic of water and is an expression of the amount of light that is scattered by material in the water when a light is shined through the water sample. The higher the intensity of scattered light, the higher the turbidity. That measurement of turbidity is important test of water quality. |
|
 TDS (Total dissolved solids) Total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in a liquid. This includes anything present in the water other than the pure H20 molecules. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be a general indicator of water quality. Therefore, High TDS means many substances in the water. Unit:parts per million (ppm). |
 |
| pH hydrogen ion concentration In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
 |
 |
|
Chlorine Residual That portion of the total available chlorine residual remaining in water or wastewater at the end of a specified contact period. Chlorine residual will react chemically and biologically as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) or hypochlorite ion (OCl–). This does not include chlorine that has combined with ammonia, nitrogen, or other compounds. 1. At 30 minutes after the addition of sodium hypochlorite there should be no more than 2.0 mg/L of free chlorine residua l present (this ensures the water does not have an unpleasant taste or odor). 2. At 24 hours after the addition of sodium hypochlorite to containers that are used by families to store water there should be a minimum of 0.2 mg/L of free chlorine residual present (this ensures microbiologically clean water). |
 |
 |
|
Hard Water Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. Water is an excellent solvent and readily dissolves minerals it comes in contact with. As water moves through soil and rock, it dissolves very small amounts of minerals and holds them in solution. Calcium and magnesium dissolved in water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard." |
 |
 |
|
Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of relative clarity of a liquid. It means the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is an optical characteristic of water and is an expression of the amount of light that is scattered by material in the water when a light is shined through the water sample. The higher the intensity of scattered light, the higher the turbidity. That measurement of turbidity is important test of water quality. |
 |
|
 |
|
 TDS (Total dissolved solids) Total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in a liquid. This includes anything present in the water other than the pure H20 molecules. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be a general indicator of water quality. Therefore, High TDS means many substances in the water. Unit:parts per million (ppm). |
 |
| pH hydrogen ion concentration In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
 |
 |
|
Chlorine Residual That portion of the total available chlorine residual remaining in water or wastewater at the end of a specified contact period. Chlorine residual will react chemically and biologically as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) or hypochlorite ion (OCl–). This does not include chlorine that has combined with ammonia, nitrogen, or other compounds. 1. At 30 minutes after the addition of sodium hypochlorite there should be no more than 2.0 mg/L of free chlorine residua l present (this ensures the water does not have an unpleasant taste or odor). 2. At 24 hours after the addition of sodium hypochlorite to containers that are used by families to store water there should be a minimum of 0.2 mg/L of free chlorine residual present (this ensures microbiologically clean water). |
 |
 |
|
Hard Water Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. Water is an excellent solvent and readily dissolves minerals it comes in contact with. As water moves through soil and rock, it dissolves very small amounts of minerals and holds them in solution. Calcium and magnesium dissolved in water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard." |
 |
 |
|
Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of relative clarity of a liquid. It means the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is an optical characteristic of water and is an expression of the amount of light that is scattered by material in the water when a light is shined through the water sample. The higher the intensity of scattered light, the higher the turbidity. That measurement of turbidity is important test of water quality. |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 TDS (Total dissolved solids) Total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in a liquid. This includes anything present in the water other than the pure H20 molecules. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be a general indicator of water quality. Therefore, High TDS means many substances in the water. Unit:parts per million (ppm). |
 |
| pH hydrogen ion concentration In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. |
 |
 |
|
Chlorine Residual That portion of the total available chlorine residual remaining in water or wastewater at the end of a specified contact period. Chlorine residual will react chemically and biologically as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) or hypochlorite ion (OCl–). This does not include chlorine that has combined with ammonia, nitrogen, or other compounds. 1. At 30 minutes after the addition of sodium hypochlorite there should be no more than 2.0 mg/L of free chlorine residua l present (this ensures the water does not have an unpleasant taste or odor). 2. At 24 hours after the addition of sodium hypochlorite to containers that are used by families to store water there should be a minimum of 0.2 mg/L of free chlorine residual present (this ensures microbiologically clean water). |
 |
 |
|
Hard Water Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. Water is an excellent solvent and readily dissolves minerals it comes in contact with. As water moves through soil and rock, it dissolves very small amounts of minerals and holds them in solution. Calcium and magnesium dissolved in water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard." |
 |
 |
|
Turbidity Turbidity is the measure of relative clarity of a liquid. It means the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is an optical characteristic of water and is an expression of the amount of light that is scattered by material in the water when a light is shined through the water sample. The higher the intensity of scattered light, the higher the turbidity. That measurement of turbidity is important test of water quality. |




